22 November, 2023
All About Exact HPE7-A01 Exam Dumps
It is more faster and easier to pass the HP HPE7-A01 exam by using Exact HP Aruba Certified Campus Access Professional Exam questuins and answers. Immediate access to the Up to the immediate present HPE7-A01 Exam and find the same core area HPE7-A01 questions with professionally verified answers, then PASS your exam with a high score now.
Question 1
DRAG DROP
Select the Aruba stacking technology matching each option (Options may be used more than once or not at all.)

Solution:
a) Support up to 10 devices per stack -> VSF
b) Support two devices per stack -> VSX
c) Individual ISL links up to 400G are supported -> VSX
d) individual ISL links up to 50G are supported -> VSF
e) A maximum aggregate ISL bandwidth of 200G is supported -> VSF
References: 1 https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.04/HTML/5200-6728/GUID-2E425DAE-EC54-4313-9DEA-A61817F903C0.html
Does this meet the goal?
Select the Aruba stacking technology matching each option (Options may be used more than once or not at all.)

Solution:
a) Support up to 10 devices per stack -> VSF
b) Support two devices per stack -> VSX
c) Individual ISL links up to 400G are supported -> VSX
d) individual ISL links up to 50G are supported -> VSF
e) A maximum aggregate ISL bandwidth of 200G is supported -> VSF
References: 1 https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.04/HTML/5200-6728/GUID-2E425DAE-EC54-4313-9DEA-A61817F903C0.html
Does this meet the goal?
Question 2
By default, Best Effort is higher priority than which priority traffic type?
Question 3
DRAG DROP
List the WPA 4-Way Handshake functions in the correct order.
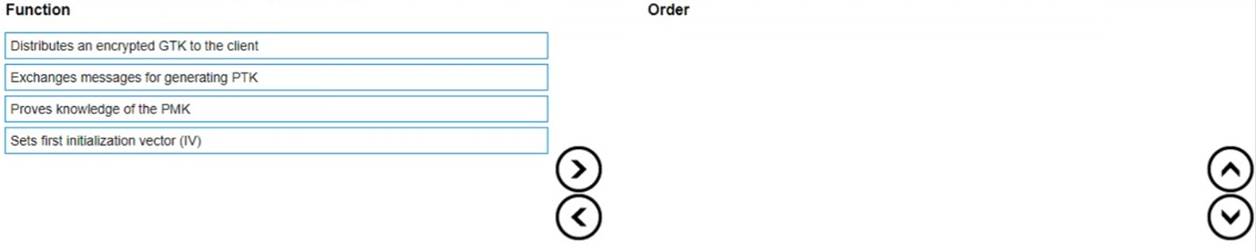
Solution:
✑ Proves knowledge of the PMK
✑ Exchanges messages for generating PTK
✑ Distributes an encrypted GTK to the client
✑ Sets first initialization vector (IV)
Does this meet the goal?
List the WPA 4-Way Handshake functions in the correct order.

Solution:
✑ Proves knowledge of the PMK
✑ Exchanges messages for generating PTK
✑ Distributes an encrypted GTK to the client
✑ Sets first initialization vector (IV)
Does this meet the goal?
Question 4
In an ArubaOS 10 architecture using an AP and a gateway, what happens when a client attempts to join the network and the WLAN is configured with OWE?
Question 5
What are the requirements to ensure that WMM is working effectively'? (Select two)
Question 6
The customer needs a network hardware refresh to replace an aging Aruba 5406R core switch pair using spanning tree configuration with Aruba CX 8360-32YC switches What is the benefit of VSX clustering with the new solution?
Question 7
A customer has a site with 200 AP-515 access points 75AP-565 access points installed.
The customer is rolling out new mobile phones with Wi-Fi-calling. 802.1X is in use for authentication
What should be enabled to ensure the best roaming experience?
The customer is rolling out new mobile phones with Wi-Fi-calling. 802.1X is in use for authentication
What should be enabled to ensure the best roaming experience?
Question 8
A company recently deployed new Aruba Access Points at different branch offices Wireless 802.1X authentication will be against a RADIUS server in the cloud. The security team is concerned that the traffic between the AP and the RADIUS server will be exposed.
What is the appropriate solution for this scenario?
What is the appropriate solution for this scenario?
Question 9
Your manufacturing client is deploying two hundred wireless IP cameras and fifty headless scanners in their warehouse. These new devices do not support 802.1X authentication.
How can HPE Aruba enhance security for these new IP cameras in this environment?
How can HPE Aruba enhance security for these new IP cameras in this environment?
Question 10
You need to have different routing-table requirements with Aruba CX 6300 VSF configuration
Assuming the correct layer-2 VLAN already exists how would you create a new OSPF configuration for a separate routing table?
Assuming the correct layer-2 VLAN already exists how would you create a new OSPF configuration for a separate routing table?
Question 11
Your Director of Security asks you to assign AOS-CX switch management roles to new employees based on their specific job requirements. After the configuration was complete, it was noted that a user assigned with the auditors role did not have the appropriate level of access on the switch.
The user was not allowed to perform firmware upgrades and a privilege level of 15 was not assigned to their role. Which default management role should have been assigned for the user?
The user was not allowed to perform firmware upgrades and a privilege level of 15 was not assigned to their role. Which default management role should have been assigned for the user?
Question 12
A new network design is being considered to minimize client latency in a high-density environment. The design needs to do this by eliminating contention overhead by dedicating subcarriers to clients.
Which technology is the best match for this use case?
Which technology is the best match for this use case?
Question 13
Which feature supported by SNMPv3 provides an advantage over SNMPv2c?
Question 14
With the Aruba CX 6100 48G switch with uplinks of 1/1/47 and 1/1/48. how do you automate the process of resuming the port operational state once a loop on a client port is cleared?
Question 15
A customer is using Aruba Cloud Guest, but visitors keep complaining that the captive portal page keeps coming up after devices go to sleep Which solution should be enabled to deal with this issue?
Question 16
A network administrator is attempting to troubleshoot a connectivity issue between a group of users and a particular server The administrator needs to examine the packets over a period of time from their desktop; however, the administrator is not directly connected to the AOS-CX switch involved with the traffic flow.
What statements are correct regarding the ERSPAN session that needs to be established on an AOS-CX switch'? (Select two )
What statements are correct regarding the ERSPAN session that needs to be established on an AOS-CX switch'? (Select two )
Question 17
A customer is using a legacy application that communicates at layer-2. The customer would like to keep this application working to a remote site connected via layer-3 All legacy devices are connected to a dedicated Aruba CX 6200 switch at each site.
What technology on the Aruba CX 6200 could be used to meet this requirement?
What technology on the Aruba CX 6200 could be used to meet this requirement?
Question 18
In AOS 10. which session-based ACL below will only allow ping from any wired station to wireless clients but will not allow ping from wireless clients to wired stations"? The wired host ingress traffic arrives on a trusted port.
Question 19
With the Aruba CX 6200 24G switch with uplinks or 1/1/25 and 1/1/26, how do you protect client ports from forming layer-2 loops?
Question 20
A company deployed Dynamic Segmentation with their CX switches and Gateways After performing a security audit on their network, they discovered that the tunnels built between the CX switch and the Aruba Gateway are not encrypted. The company is concerned that bad actors could try to insert spoofed messages on the Gateway to disrupt communications or obtain information about the network.
Which action must the administrator perform to address this situation?
Which action must the administrator perform to address this situation?
Question 21
Your customer is having issues with Wi-Fi 6 clients staying connected to poor-performing APs when a higher throughput APs are closer. Which technology should you implement?
Question 22
For the Aruba CX 6400 switch, what does virtual output queueing (VOQ) implement that is different from most typical campus switches?
Question 23
Two AOS-CX switches are configured with VSX at the the Access-Aggregation layer where servers attach to them An SVI interface is configured for VLAN 10 and serves as the default gateway for VLAN 10. The ISL link between the switches fails, but the keepalive interface functions. Active gateway has been configured on the VSX switches.
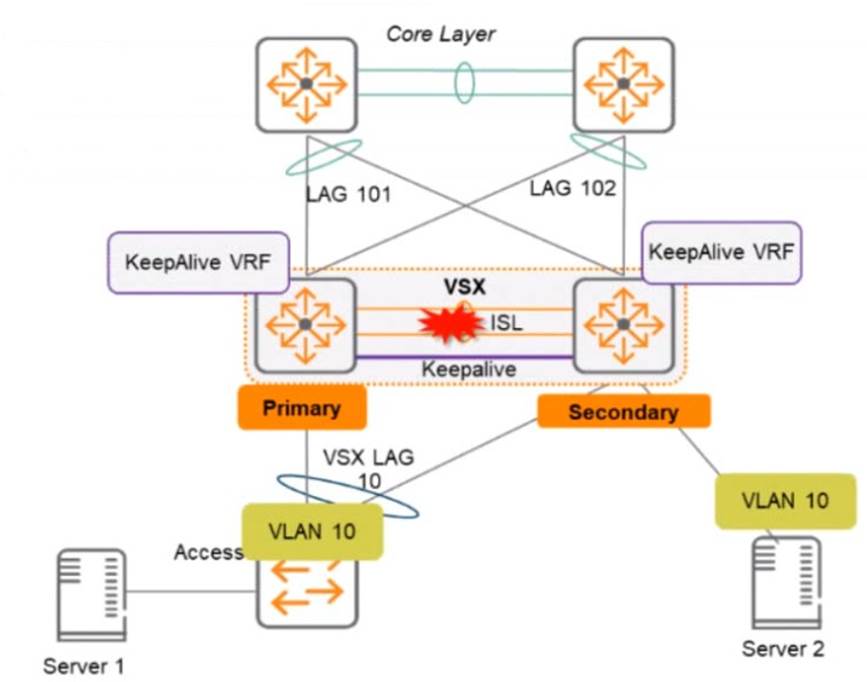
What is correct about access from the servers to the Core? (Select two.)

What is correct about access from the servers to the Core? (Select two.)
Question 24
Which statements are true regarding a VXLAN implementation on Aruba Switches? (Select two.)
Question 25
When setting up an Aruba CX VSX pair, which information does the Inter-Switch Link Protocol configuration use in the configuration created?
Question 26
Which Aruba AP mode is sending captured RF data to Aruba Central for waterfall plot?
Question 27
When setting up an Aruba CX VSX pair, which information does the Inter-Switch Link Protocol configuration use in the configuration created?
Question 28
A large retail client is looking to generate a rich set of contextual data based on the location information of wireless clients in their stores Which standard uses Round Trip Time (RTT) and Fine Time Measurements (FTM) to calculate the distance a client is from an AP?
Question 29
You need to create a keepalive network between two Aruba CX 8325 switches for VSX configuration How should you establish the keepalive connection?
Question 30
You are are doing tests in your lab and with the following equipment specifications:
• AP1 has a radio that generates a 16 dBm signal.
• AP2 has a radio that generates a 13 dBm signal.
• AP1 has an antenna with a gain of 8 dBi.
• AP2 has an antenna with a gain of 12 dBi. The antenna cable for AP1 has a 4 dB loss. The antenna cable for AP2 has a 3 dB loss.
What would be the calculated Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) for AP1?
• AP1 has a radio that generates a 16 dBm signal.
• AP2 has a radio that generates a 13 dBm signal.
• AP1 has an antenna with a gain of 8 dBi.
• AP2 has an antenna with a gain of 12 dBi. The antenna cable for AP1 has a 4 dB loss. The antenna cable for AP2 has a 3 dB loss.
What would be the calculated Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) for AP1?
