29 December, 2019
Implementing Cisco IP Routing 300-101 Samples
Pass4sure 300-101 Questions are updated and all 300-101 answers are verified by experts. Once you have completely prepared with our 300-101 exam prep kits you will be ready for the real 300-101 exam without a problem. We have Up to the immediate present Cisco 300-101 dumps study guide. PASSED 300-101 First attempt! Here What I Did.
Question 1
Which LSA types can exist only in an OSPF NSSA area?
Question 2
Which three benefits does the Cisco Easy Virtual Network provide to an enterprise network? (Choose three)
Question 3
Which two statements are examples of the difference between IPV4 and IPV6 EIGRP? (Choose two)
Question 4
Which Cisco Express Forwarding component maintains the Layer 2 next-hop addresses that are used for hardware switching?
Question 5
Which action is one way to mitigate asymmetric routing on an active/active firewall setup foi TCP-based connections'?
Question 6
Which feature can be used to reduce the number of ICMP unreachable messages egressing a router?
Question 7
Which statements best describes the following two OSPF commands, which are used to summarize routes? area 0 range 192.168.110.0 255.255.0.0
summary-address 192.168.110.0 255.255.0.0
summary-address 192.168.110.0 255.255.0.0
Question 8
A network engineer wants to implement an SNMP notification process for host machines using the strongest security available Which command accomplishes this task?
Question 9
If routers in a single area are configured with the same priority value, what value does a router use for the OSPF Router ID in the absence of a loopback interface?
Question 10
Which statement about conditional debugging is true?
Question 11
A customer asks its service provider for VPN support for IPv4 and IPv6 address families Which command enables a VRF that supports these requirements?
Question 12
A network engineer executes the show ip flow interface command. Which type of information is displayed on
the interface?
the interface?
Question 13
Which two statements about GRE tunnel interfaces are true? (Choose two)
Question 14
Which two actions are common methods for migrating a network from one network protocol to another? (choose two)
Question 15
Which two steps must you perform to allow access to a device when the connection to a remote TACACS+ authentication server fails? (Choose two)
Question 16
Which IOS commands can you use to limit the CPU impact of log generation and transmission on an IOS router?
Question 17
Which command can be entered on router R5 to configure 80 percent of the bandwidth of a link for EIGRP Autonomous System 55?
Question 18
Which option is an invalid redistribute command option for redistributing routes from EIGRPintoOSPF?
Question 19
Which type of message does a device configured with the eigrp stub command send in response to EIGRP queries?
Question 20
Drag and drop the statement about device security from the left on the correct features on the right.
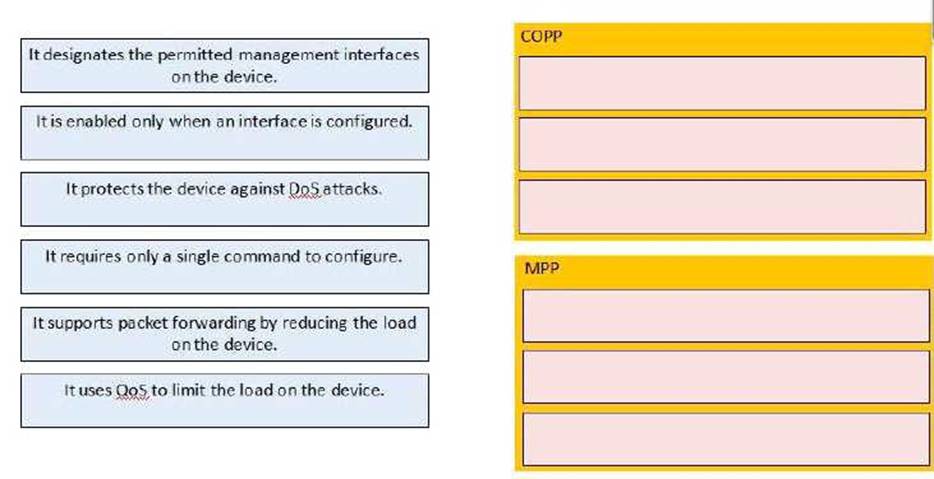
Solution:
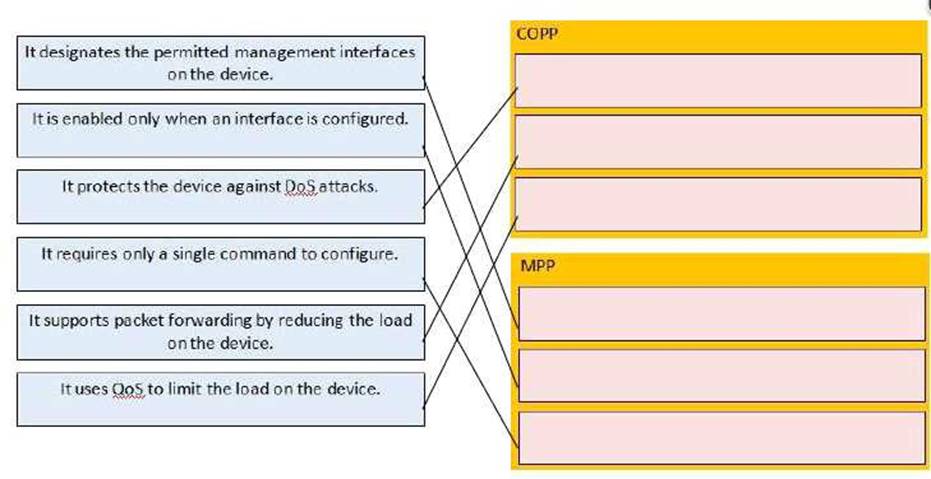
Does this meet the goal?

Solution:

Does this meet the goal?
Question 21
Which protocol does VRF-Lite support?
Question 22
Which types of LSAs are present in the stub area?
Question 23
WHICH COMMAND DO YOU ENTER ON ROUTER R6 SO THAT BGP SUPPORTS MULTIPLE PROTOCOLS?
Question 24
Which issue is important to address when integrating two networks with different routing protocols?
Question 25
Refer to the exhibit.
Which networking challenge is the most important issue to address to enable optimal communication between the networks at Company A and Company B?
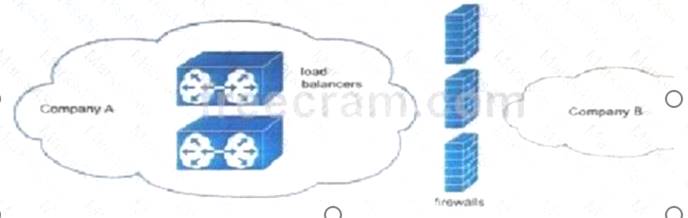
Which networking challenge is the most important issue to address to enable optimal communication between the networks at Company A and Company B?

Question 26
JS Industries has expanded their business with the addition of their first remote office. The remote office router (R3) was previously configured and all Corporate subnets were reachable from R3. JS Industries is interested in using route summarization along with the EIGRP Stub Routing feature to increase network stability while reducing the memory usage and bandwidth utilization to R3. Another network professional was tasked with implementing this solution. However, in the process of configuring EIGRP stub routing connectivity with the remote network devices off of R3 has been lost.
Currently EIGRP is configured on all routers R2, R3, and R4 in the network. Your task is to identify and resolve the cause of connectivity failure with the remote office router R3. Once the issue has been resolved you should complete the task by configuring route summarization only to the remote office router R3.
You have corrected the fault when pings from R2 to the R3 LAN interface are successful, and the R3 IP routing table only contains 2 10.0.0.0 subnets.
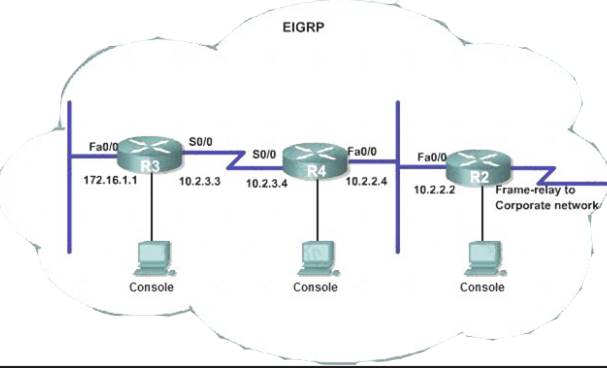
Solution:
First we have to figure out why R3 and R4 can not communicate with each other. Use the show running-config command on router R3.
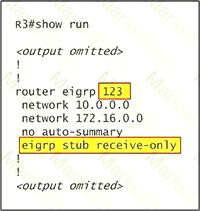
Notice that R3 is configured as a stub receive-only router. The receive-only keyword will restrict the router from sharing any of its routes with any other router in that EIGRP autonomous system. This keyword will also prevent any type of route from being sent. Therefore we will remove this command and replace it with the eigrp stub command:
R3# configure terminal R3(config)# router eigrp 123 R3(config-router)# no eigrp stub receive-only R3(config-router)# eigrp stub
R3(config-router)# end
Now R3 will send updates containing its connected and summary routes to other routers. Notice that the eigrp stub command equals to the eigrp stub connected summary because the connected and summary options are enabled by default.
Next we will configure router R3 so that it has only 2 subnets of 10.0.0.0 network. Use the show ip route command on R3 to view its routing table:
[ee1%255B5%255D.jpg]
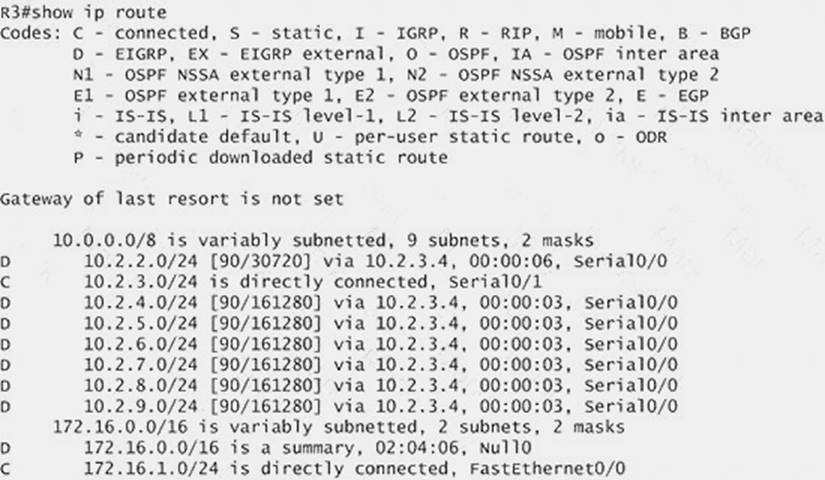
Because we want the routing table of R3 only have 2 subnets so we have to summary sub-networks at the interface which is connected with R3, the s0/0 interface of R4.
There is one interesting thing about the output of the show ip route shown above: the 10.2.3.0/24, which is a directly connected network of R3. We can’t get rid of it in the routing table no matter what technique we use to summary the networks. Therefore, to make the routing table of R3 has only 2 subnets we have to summary other subnets into one subnet.
In the output if we don’t see the summary line (like 10.0.0.0/8 is a summary…) then we should use the command ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 so that all the ping can work well.
In conclusion, we will use the ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 at the interface s0/0 of R4 to summary.
R4> enable R4# conf t
R4(config)# interface s0/0 R4(config-if)# ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0
Now we jump back to R3 and use the show ip route command to verify the effect, the output is shown below: [ee2%255B5%255D.jpg]
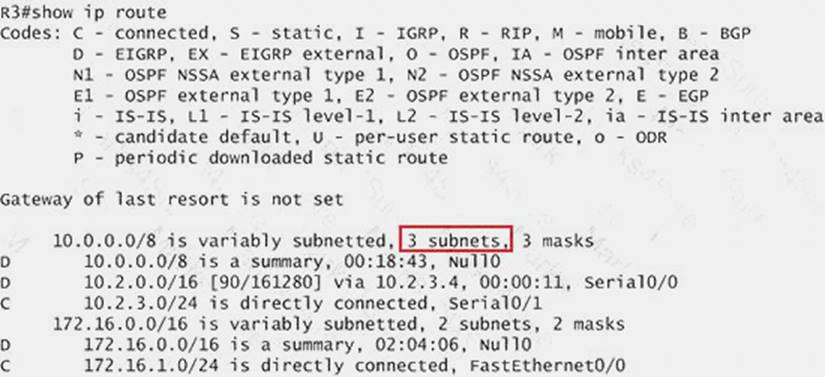
Note: Please notice that the IP addresses and the subnet masks in your real exam might be different so you might use different ones to solve this question.
Just for your information, notice that if you use another network than 10.0.0.0/8 to summary, for example, if you use the command ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 you will leave a /16 network in the output of the show ip route command.
[ee3%255B5%255D.jpg]
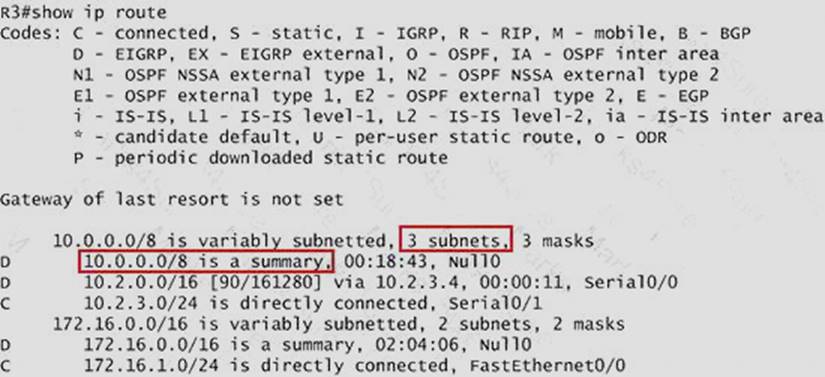
But in your real exam, if you don’t see the line "10.0.0.0/8 is a summary, Null0" then you can summarize using the network 10.2.0.0/16. This summarization is better because all the pings can work well.
Finally don’t forget to use the copy run start command on routers R3 and R4 to save the configurations. R3(config-if)# end
R3# copy run start R4(config-if)# end R4# copy run start
If the “copy run start” command doesn’t work then use “write memory”.
Does this meet the goal?
Currently EIGRP is configured on all routers R2, R3, and R4 in the network. Your task is to identify and resolve the cause of connectivity failure with the remote office router R3. Once the issue has been resolved you should complete the task by configuring route summarization only to the remote office router R3.
You have corrected the fault when pings from R2 to the R3 LAN interface are successful, and the R3 IP routing table only contains 2 10.0.0.0 subnets.




Solution:
First we have to figure out why R3 and R4 can not communicate with each other. Use the show running-config command on router R3.

Notice that R3 is configured as a stub receive-only router. The receive-only keyword will restrict the router from sharing any of its routes with any other router in that EIGRP autonomous system. This keyword will also prevent any type of route from being sent. Therefore we will remove this command and replace it with the eigrp stub command:
R3# configure terminal R3(config)# router eigrp 123 R3(config-router)# no eigrp stub receive-only R3(config-router)# eigrp stub
R3(config-router)# end
Now R3 will send updates containing its connected and summary routes to other routers. Notice that the eigrp stub command equals to the eigrp stub connected summary because the connected and summary options are enabled by default.
Next we will configure router R3 so that it has only 2 subnets of 10.0.0.0 network. Use the show ip route command on R3 to view its routing table:
[ee1%255B5%255D.jpg]

Because we want the routing table of R3 only have 2 subnets so we have to summary sub-networks at the interface which is connected with R3, the s0/0 interface of R4.
There is one interesting thing about the output of the show ip route shown above: the 10.2.3.0/24, which is a directly connected network of R3. We can’t get rid of it in the routing table no matter what technique we use to summary the networks. Therefore, to make the routing table of R3 has only 2 subnets we have to summary other subnets into one subnet.
In the output if we don’t see the summary line (like 10.0.0.0/8 is a summary…) then we should use the command ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 so that all the ping can work well.
In conclusion, we will use the ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 at the interface s0/0 of R4 to summary.
R4> enable R4# conf t
R4(config)# interface s0/0 R4(config-if)# ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0
Now we jump back to R3 and use the show ip route command to verify the effect, the output is shown below: [ee2%255B5%255D.jpg]

Note: Please notice that the IP addresses and the subnet masks in your real exam might be different so you might use different ones to solve this question.
Just for your information, notice that if you use another network than 10.0.0.0/8 to summary, for example, if you use the command ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 you will leave a /16 network in the output of the show ip route command.
[ee3%255B5%255D.jpg]

But in your real exam, if you don’t see the line "10.0.0.0/8 is a summary, Null0" then you can summarize using the network 10.2.0.0/16. This summarization is better because all the pings can work well.
Finally don’t forget to use the copy run start command on routers R3 and R4 to save the configurations. R3(config-if)# end
R3# copy run start R4(config-if)# end R4# copy run start
If the “copy run start” command doesn’t work then use “write memory”.
Does this meet the goal?
