12 October, 2022
Replace 312-50v12 Braindumps For Certified Ethical Hacker Exam (CEHv12) Certification
Your success in EC-Council 312-50v12 is our sole target and we develop all our 312-50v12 braindumps in a way that facilitates the attainment of this target. Not only is our 312-50v12 study material the best you can find, it is also the most detailed and the most updated. 312-50v12 Practice Exams for EC-Council 312-50v12 are written to the highest standards of technical accuracy.
Question 1
A pen tester is configuring a Windows laptop for a test. In setting up Wireshark, what river and library are required to allow the NIC to work in promiscuous mode?
Question 2
Hackers often raise the trust level of a phishing message by modeling the email to look similar to the internal email used by the target company. This includes using logos, formatting, and names of the target company. The phishing message will often use the name of the company CEO, President, or Managers. The time a hacker spends performing research to locate this information about a company is known as?
Question 3
John wants to send Marie an email that includes sensitive information, and he does not trust the network that he is connected to. Marie gives him the idea of using PGP. What should John do to communicate correctly using this type of encryption?
Question 4
Attacker Steve targeted an organization's network with the aim of redirecting the company's web traffic to another malicious website. To achieve this goal, Steve performed DNS cache poisoning by exploiting the vulnerabilities In the DNS server software and modified the original IP address of the target website to that of a fake website. What is the technique employed by Steve to gather information for identity theft?
Question 5
which of the following protocols can be used to secure an LDAP service against anonymous queries?
Question 6
To invisibly maintain access to a machine, an attacker utilizes a toolkit that sits undetected In the core components of the operating system. What is this type of rootkit an example of?
Question 7
Samuel a security administrator, is assessing the configuration of a web server. He noticed that the server permits SSlv2 connections, and the same private key certificate is used on a different server that allows SSLv2 connections. This vulnerability makes the web server vulnerable to attacks as the SSLv2 server can leak key information.
Which of the following attacks can be performed by exploiting the above vulnerability?
Which of the following attacks can be performed by exploiting the above vulnerability?
Question 8
Johnson, an attacker, performed online research for the contact details of reputed cybersecurity firms. He found the contact number of sibertech.org and dialed the number, claiming himself to represent a technical support team from a vendor. He warned that a specific server is about to be compromised and requested sibertech.org to follow the provided instructions. Consequently, he prompted the victim to execute unusual commands and install malicious files, which were then used to collect and pass critical Information to Johnson's machine. What is the social engineering technique Steve employed in the above scenario?
Question 9
Consider the following Nmap output:
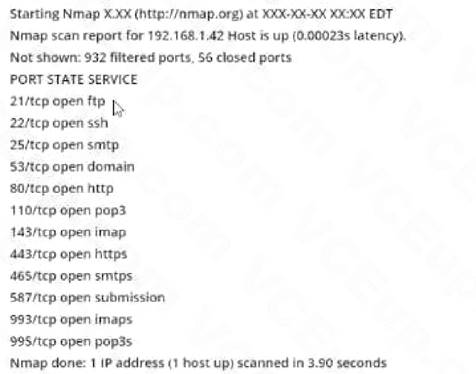
what command-line parameter could you use to determine the type and version number of the web server?

what command-line parameter could you use to determine the type and version number of the web server?
Question 10
Mary found a high vulnerability during a vulnerability scan and notified her server team. After analysis, they sent her proof that a fix to that issue had already been applied. The vulnerability that Marry found is called what?
Question 11
in this attack, an adversary tricks a victim into reinstalling an already-in-use key. This is achieved by manipulating and replaying cryptographic handshake messages. When the victim reinstall the key, associated parameters such as the incremental transmit packet number and receive packet number are reset to their initial values. What is this attack called?
Question 12
which of the following information security controls creates an appealing isolated environment for hackers to prevent them from compromising critical targets while simultaneously gathering information about the hacker?
Question 13
Wilson, a professional hacker, targets an organization for financial benefit and plans to compromise its systems by sending malicious emails. For this purpose, he uses a tool to track the emails of the target and extracts information such as sender identities, mall servers, sender IP addresses, and sender locations from different public sources. He also checks if an email address was leaked using the haveibeenpwned.com API. Which of the following tools is used by Wilson in the above scenario?
Question 14
What is the first step for a hacker conducting a DNS cache poisoning (DNS spoofing) attack against an organization?
Question 15
Which rootkit is characterized by its function of adding code and/or replacing some of the operating-system kernel code to obscure a backdoor on a system?
Question 16
What is the following command used for?
sqlmap.py-u
,,http://10.10.1.20/?p=1
&forumaction=search" -dbs
sqlmap.py-u
,,http://10.10.1.20/?p=1
&forumaction=search" -dbs
Question 17
Boney, a professional hacker, targets an organization for financial benefits. He performs an attack by sending his session ID using an MITM attack technique. Boney first obtains a valid session ID by logging into a service and later feeds the same session 10 to the target employee. The session ID links the target employee to Boneys account page without disclosing any information to the victim. When the target employee clicks on the link, all the sensitive payment details entered in a form are linked to Boneys account. What is the attack performed by Boney in the above scenario?
Question 18
Bob, an attacker, has managed to access a target loT device. He employed an online tool to gather information related to the model of the loT device and the certifications granted to it. Which of the following tools did Bob employ to gather the above Information?



