10 January, 2024
What 100% Correct SSCP Practice Exam Is
It is more faster and easier to pass the ISC2 SSCP exam by using Validated ISC2 System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) questuins and answers. Immediate access to the Replace SSCP Exam and find the same core area SSCP questions with professionally verified answers, then PASS your exam with a high score now.
Online SSCP free questions and answers of New Version:
Question 1
- (Topic 5)
Which of the following is not a DES mode of operation?
Which of the following is not a DES mode of operation?
Question 2
- (Topic 5)
Which of the following concerning the Rijndael block cipher algorithm is false?
Which of the following concerning the Rijndael block cipher algorithm is false?
Question 3
- (Topic 1)
The number of violations that will be accepted or forgiven before a violation record is produced is called which of the following?
The number of violations that will be accepted or forgiven before a violation record is produced is called which of the following?
Question 4
- (Topic 1)
What is called the percentage at which the False Rejection Rate equals the False Acceptance Rate?
What is called the percentage at which the False Rejection Rate equals the False Acceptance Rate?
Question 5
- (Topic 1)
In the context of access control, locks, gates, guards are examples of which of the following?
In the context of access control, locks, gates, guards are examples of which of the following?
Question 6
- (Topic 4)
Under the Business Exemption Rule to the hearsay evidence, which of the following exceptions would have no bearing on the inadmissibility of audit logs and audit trails in a court of law?
Under the Business Exemption Rule to the hearsay evidence, which of the following exceptions would have no bearing on the inadmissibility of audit logs and audit trails in a court of law?
Question 7
- (Topic 2)
What prevents a process from accessing another process' data?
What prevents a process from accessing another process' data?
Question 8
- (Topic 6)
In the context of network enumeration by an outside attacker and possible Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which of the following firewall rules is not appropriate to protect an organization's internal network?
In the context of network enumeration by an outside attacker and possible Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which of the following firewall rules is not appropriate to protect an organization's internal network?
Question 9
- (Topic 6)
Which of the following is an IP address that is private (i.e. reserved for internal networks, and not a valid address to use on the Internet)?
Which of the following is an IP address that is private (i.e. reserved for internal networks, and not a valid address to use on the Internet)?
Question 10
- (Topic 6)
Which of the following is the biggest concern with firewall security?
Which of the following is the biggest concern with firewall security?
Question 11
- (Topic 6)
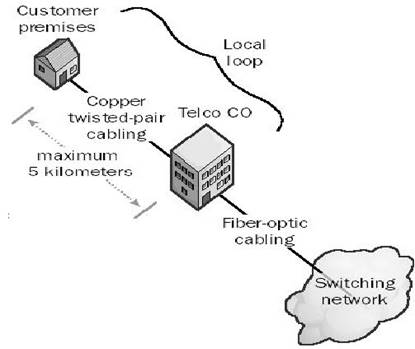
In telephony different types of connections are being used. The connection from the phone company's branch office to local customers is referred to as which of the following choices?
In telephony different types of connections are being used. The connection from the phone company's branch office to local customers is referred to as which of the following choices?
Question 12
- (Topic 1)
Which of the following statements pertaining to RADIUS is incorrect:
Which of the following statements pertaining to RADIUS is incorrect:
Question 13
- (Topic 2)
What is the goal of the Maintenance phase in a common development process of a security policy?
What is the goal of the Maintenance phase in a common development process of a security policy?
Question 14
- (Topic 5)
What is the name of the third party authority that vouches for the binding between the data items in a digital certificate?
What is the name of the third party authority that vouches for the binding between the data items in a digital certificate?
Question 15
- (Topic 2)
Which of the following statements pertaining to software testing approaches is correct?
Which of the following statements pertaining to software testing approaches is correct?
Question 16
- (Topic 6)
How do you distinguish between a bridge and a router?
How do you distinguish between a bridge and a router?
Question 17
- (Topic 4)
In which of the following phases of system development life cycle (SDLC) is contingency planning most important?
In which of the following phases of system development life cycle (SDLC) is contingency planning most important?
Question 18
- (Topic 1)
What can be defined as a list of subjects along with their access rights that are authorized to access a specific object?
What can be defined as a list of subjects along with their access rights that are authorized to access a specific object?
Question 19
- (Topic 5)
What kind of certificate is used to validate a user identity?
What kind of certificate is used to validate a user identity?
Question 20
- (Topic 4)
When a possible intrusion into your organization's information system has been detected, which of the following actions should be performed first?
When a possible intrusion into your organization's information system has been detected, which of the following actions should be performed first?
Question 21
- (Topic 1)
Which of the following is NOT an advantage that TACACS+ has over TACACS?
Which of the following is NOT an advantage that TACACS+ has over TACACS?
Question 22
- (Topic 5)
Compared to RSA, which of the following is true of Elliptic Curve Cryptography(ECC)?
Compared to RSA, which of the following is true of Elliptic Curve Cryptography(ECC)?